UI/UX design tools—or, what you can also call User Interface design tools and User Experience design tools—are those specialized software applications that help designers create, modify, and explore user interfaces and user experiences. But they’re more than just software—they’re like bridges in a sense, or a way for you, dear designer, to turn abstract concepts into solid design solutions that your brand’s users will (ideally) be delighted with and keep coming back to. To help you out choices-wise, we’ve put together a little “best of” list that features some top UX and UI design tools for 2025, so be sure to keep on reading.
Table of contents
- Why Do You Need UX and UI Design Tools?
- What Types of UI and UX Design Tools Are There?
- What Are 3 Key Factors to Choose UI and UX Design Tools?
- What Are Tips and Best Practices to Use UI and UX Design Tools?
- Some Top UI and UX Design Tools in 2025
- How About an In-Depth Review of a Top UX and UI Design Tool?
- The Take Away
Why Do You Need UX and UI Design Tools?
Sure enough, they’re vital parts—these tools—of a designer’s toolkit. With that said, it’s important to first be clear that what’s inside the designer’s head, as in, yours, is the most essential tool of all. You need a strong grasp of theoretical aspects like color theory and design principles if you’re to make the most of the tools you then take up to work your abstract ideas into something concrete through sketching and wireframing to prototyping and usability testing. That’s how you edge your way towards user-friendly designs that can really exceed user expectations and delight your target audience in seamless experiences that bring your brand—and design solution—to life.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
Another massive bonus—or essential benefit—of UI and UX design and prototyping tools is how they help streamline your design process. That’s because they bring design teams and other project stakeholders closer for collaboration and feedback. What’s more, design tools help you do user research so you can understand user needs, behaviors, and preferences and then leverage the insights in the name of user-centered design. From there, you can create intuitive, engaging, and effective designs that can wow target users and secure their loyalty to your brand.
Watch UX Consultant and Strategist, William Hudson explain important points about user research and why you need it.
We won’t spend long on the history of UI and UX design tools—not least since they have evolved a great deal since the early days of web design, back when designers had to rely heavily on basic graphic design software. Our era demands tools for designing complex interfaces and interactions—worlds apart from the static mockups of web pages from yesteryear. The tools mirror not just the rapid technological advancements but great shifts in user behavior, too.
Think of a favorite app for a moment and consider what life was like before it—and then reflect on how people’s expectations may have built up around that app so that it’s become the norm as a design solution for them. It could be for listening to music, ordering food, or whatever the “problem” a user may need a design solution for. Tools come into play somewhere along the way as designers and design teams work out the best solutions to make.
What Types of UI and UX Design Tools Are There?
Before we start on our list, it’s important to keep in mind some sound advice from Author and Global UX Executive, Professor Daniel Rosenberg:
You’ve got various tools that cater to different stages of the design process—ranging from wireframing to prototyping, say. Each type of tool brings unique benefits and addresses distinct challenges.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
1. Wireframing Tools
Wireframing tools are the blueprint machines of the design process, and with your wireframes you make a skeletal layout of a web page or app—to illustrate the page structure, content arrangement, and intended functionalities. And so, you set the groundwork for more detailed design work later. Wireframes are crucial tools to have in the early design stages, not least since they help clarify the project’s scope and make it easier to get ideas across to—and from—stakeholders.
Wireframing software helps speed you through the initial design phase through simple drag-and-drop elements and make wireframes, which help you visualize the layout. You can explore different layout options that much more easily and make rapid iterations to them. What’s more, wireframing tools help you establish the basic structure of your design before things get more detailed, a point that also translates to the advantage that—since they look so malleable and are relatively simple and quick things—colleagues and users can be honest about suggesting changes. That’s as opposed to feeling reluctant to criticize high-fidelity prototypes, which—being more intricate and detailed—take more time and sweat to alter.
Really the only palpable drawback of wireframes is that—because they don’t have the visual design appeal of a fully designed interface—it can be harder for stakeholders who aren’t familiar with the design process to get a picture of what the final product is going to look like.
Balsamiq and Sketch are popular choices for wireframing thanks to their simplicity and efficiency.
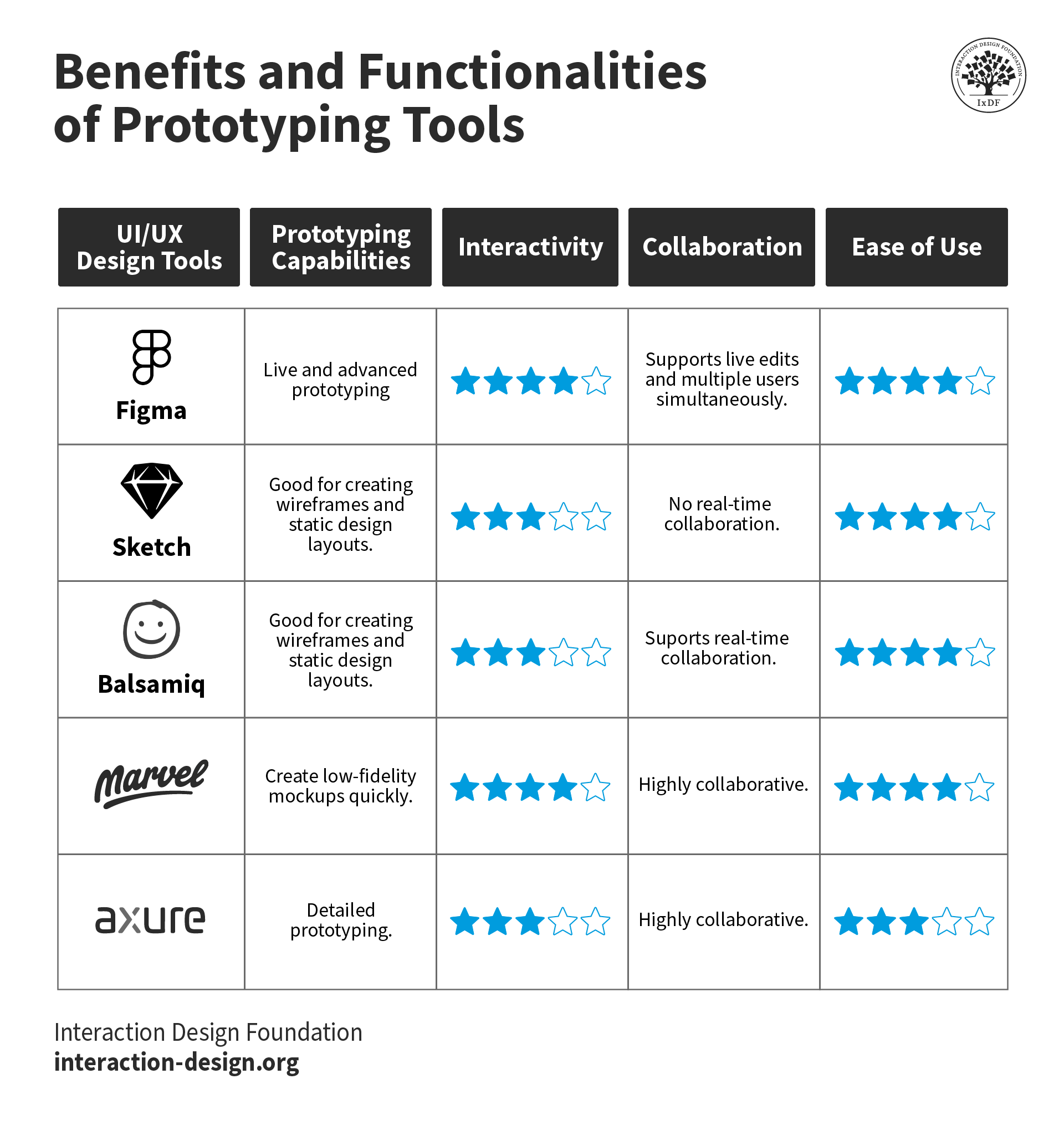
2. Prototyping Tools
Once you’ve got the basic structure of a design put into place, you can bring prototyping tools into the picture. They’re tools that let you create interactive mockups and showcase how the final product is going to work—and that includes everything from button interactions and animations to transitions and user flow.
Prototypes can give a real feel for the user experience, and the tools for them can help you a great deal when you do usability testing because they give people you give them to a hands-on experience of the design before any coding begins. So, they enable you—through your test users—to find and resolve usability issues early in the process and so lessen the risk of costly changes needing to happen later in development. Another neat plus is how prototypes help you communicate design ideas—as in, get these ideas more effectively across to stakeholders because they’ll have something set in front of them to see in more detail. And so, it will secure you better feedback from them and alignment all around.
To be sure, high-fidelity prototypes can be time-consuming to make. And then, test users might feel bad about being honest with you if there’s something wrong with a prototype they’ve got in front of them—since they’ll tend to think that you sank a great deal of time and effort into it and may not want to upset you. Aside from that, there’s also the point that some prototyping tools may be limited in how they simulate complex interactions. And it may lead to there being discrepancies between the prototype and the final product.
Figma and Axure RP have got strong reputations for what they can do for designers prototyping-wise. And they’ll provide you with a nice and wide array of interactive elements and transition effects should you pick them—so you can get into full swing with making prototypes that get results.
3. User Research Tools
If there’s one thing that’s certain in design, there’s a fair likelihood that it’ll be the research side of it. Without adequate research, designers can end up creating something that they only think will be popular and effective and helpful and—and it tanks in the marketplace because it misses the mark, slips, and tumbles into obscurity. To not trip over your assumptions, you’re going to need to do user research and get into your users’ shoes—and, to a certain degree, their heads. That’s so you can get an accurate picture of who they are and what their contexts are like if you’re to build up the empathy you’ll need to design the best solution for them.
User research tools are—suffice to say—critical instruments here, and they’re things you use to get insights about users’ behaviors, needs, and motivations. With tools that include heatmaps and card sorting, you can apply these insightfully to help you understand the user journey, find pain points, and—ultimately—craft a user experience that’s truly intuitive and satisfying for the end user.
The biggest plus as to why you should reach for user research tools is that they’ll provide you—and your design team—with data-driven insights that can inform every stage of the design process. That’s how you can create user-centric products while you keep valuable aspects about your brand’s users clearly in focus. These tools let you—or user researchers—test hypotheses, validate designs, and understand user needs and preferences in a way that’s detailed—and so in the way you need to understand your users and their realities.
To a massive degree, how effective user research tools are is largely down to the sample size and representativeness of the user group that’s involved in the research. You’ll need to appreciate the intricacies of UX research and how it takes time and resources to set up studies and analyze data, too, and how—sometimes—the data can be challenging or even overwhelming to interpret if you’ve not got the right expertise.
SurveyMonkey and Google Forms are simple, accessible tools you can use to conduct surveys, and Lookback is a solid example for user interviews. UserTesting provides audio and video feedback from users who are interacting with your designs. UX research tools like Hotjar offer you heatmaps, session recordings, and other tools for understanding user behavior on a website. Meanwhile—for early design—products such as Optimal Workshop provide card sorting, tree sorting, and first-click testing; so, there’s a good deal of options to pick from.
See our course Data-Driven Design to learn about early-design testing.
What Are 3 Key Factors to Choose UI and UX Design Tools?
1. Ease of Use
The first thing you’ll likely want to get into clear view about your potential picks of UX or UI design software is that all-important ease of use factor. An intuitive interface with straightforward functionalities can let you get right down to matters and empower you to efficiently create, iterate, and test your ideas. Pick a tool that’s got a steep learning curve, though, and it might slow you down as you get used to its various powers and intricacies. So, do think about how quickly you can adapt to a new tool as well as if it’s got a supportive community or good resources for troubleshooting and learning.
2. Features
Tool features are what people tend to go after in a big way in general—that “What’s it got?” factor being what it is. But the features that a design tool offers you should be in line with what you need for your project—you know, when you need a drill, reach for a drill, not a hammer sort of thing. And that’s why it’s vital—when you know exactly what your needs are—to match them with the right tool's features. Tools can “specialize” well in specific areas or phases of the design process, running the range across wireframing, prototyping, or what have you.
There’s a chance—or slightly more than just a chance, let’s just say—that one of your designerly tasks will find you working on high-fidelity interactive prototypes. And to make these, a tool with advanced prototyping capabilities like Figma or Axure RP is likely to be the one you want to go for. Meanwhile, when you’re working on some other things, a tool like Balsamiq or Sketch could be a neat and superb pick for you to create wireframes or static design layouts with.
3. Cost
Some design tools are free, to be sure, while others come with a cost—and that’s either as a one-time purchase or a recurring subscription fee. Perhaps oddly enough at first glance, or even counterintuitive to consider, the most expensive tool mightn’t necessarily be ideal for what you need to do. Many affordable (as in, cheaper)—or even free—tools do offer powerful functionalities and do have just the right features for what you may need them for. These may be right up your street for the task at hand. So, look at cost, sure, but remember your particular requirements in the moment for each and every thing you’ve got to do in a project. You might just surprise yourself.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
What Are Tips and Best Practices to Use UI and UX Design Tools?
Do check out those templates and UI kits because many UI and UX design tools have got pre-built templates and UI kits in them—handy reach-fors to have. You’ll find that they’re things that can fast-track your design process nicely, too, as they’ve got pre-designed components which you can customize to fit your project's needs with nice precision.
Use grids and layouts since grids—as graphic designers can attest to—are a massive help to keep things ordered. And they’re great to help keep the alignment and consistency factors going nice and strong in your design with a structured layout to help guide how you place elements so that a balanced—and organized—design can come about with less effort.
Master shortcuts because keyboard shortcuts can speed up your design process by a good amount. So, do get familiar with the shortcuts of the tool you pick so it helps you perform actions quickly—and efficiently.
Sync with a design system as a design system is a neat plus that can keep everyone on the same page if you work on a large project—or as part of a team. Plus, it sets down a shared language and set of components for all of you to enjoy a great amount of consistency across designs that you work on, too.
Prototype early and often because prototyping isn’t just a vital thing to do but something to keep doing. It's best to start prototyping early on and then to keep on iterating on your prototypes from what you find out from feedback and usability testing as you go on. And what you find may surprise you so much that you’ll be glad you course-corrected or fine-tuned things to maximum effect.
Stay organized because your design files and layers need that sense of order. It’ll make it so much easier to navigate your design, make changes, and collaborate with other people who are involved in your project—so nobody ends up asking what’s where or furrows their brow in confusion from trying to make sense of a morass of sprawl.
Keep on learning and don’t worry—it goes with the territory, since UI and UX design tools keep evolving as new features and improvements get added regularly. So, it’s more than a little wise for you, dear designer, to stay updated with the latest advancements and learn how to apply useful ones so you’ve got a sharper extra edge in your craft.
Prioritize accessibility because accessible design is a massive issue to keep in mind—and it’s the law in many jurisdictions, in fact. So, do take advantage of many design tool features that help you test and improve accessibility with big plusses like adequate color contrasts, legible fonts, and clear navigation.
Some Top UI and UX Design Tools in 2025
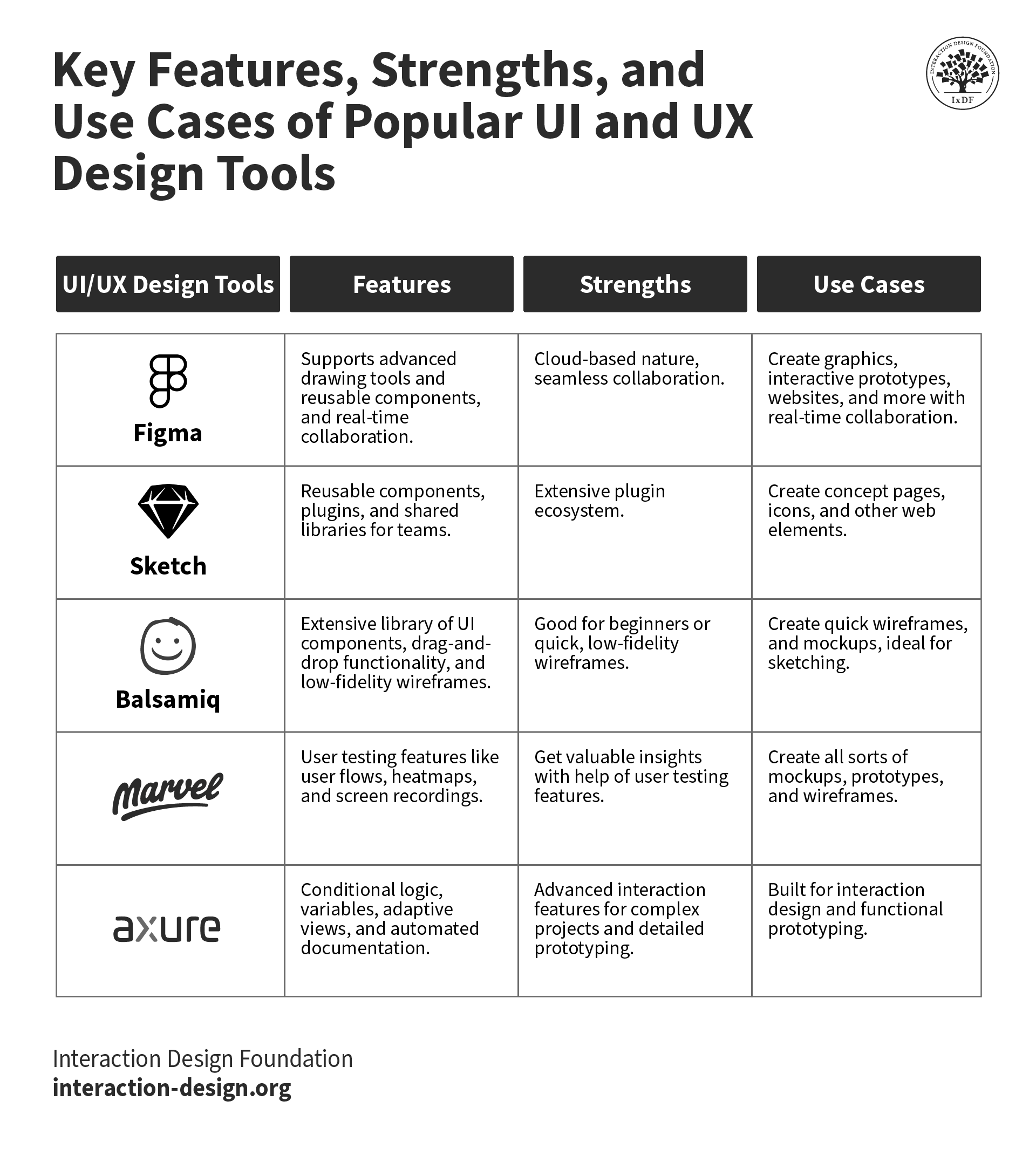
1. Figma

© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 3.0 Source
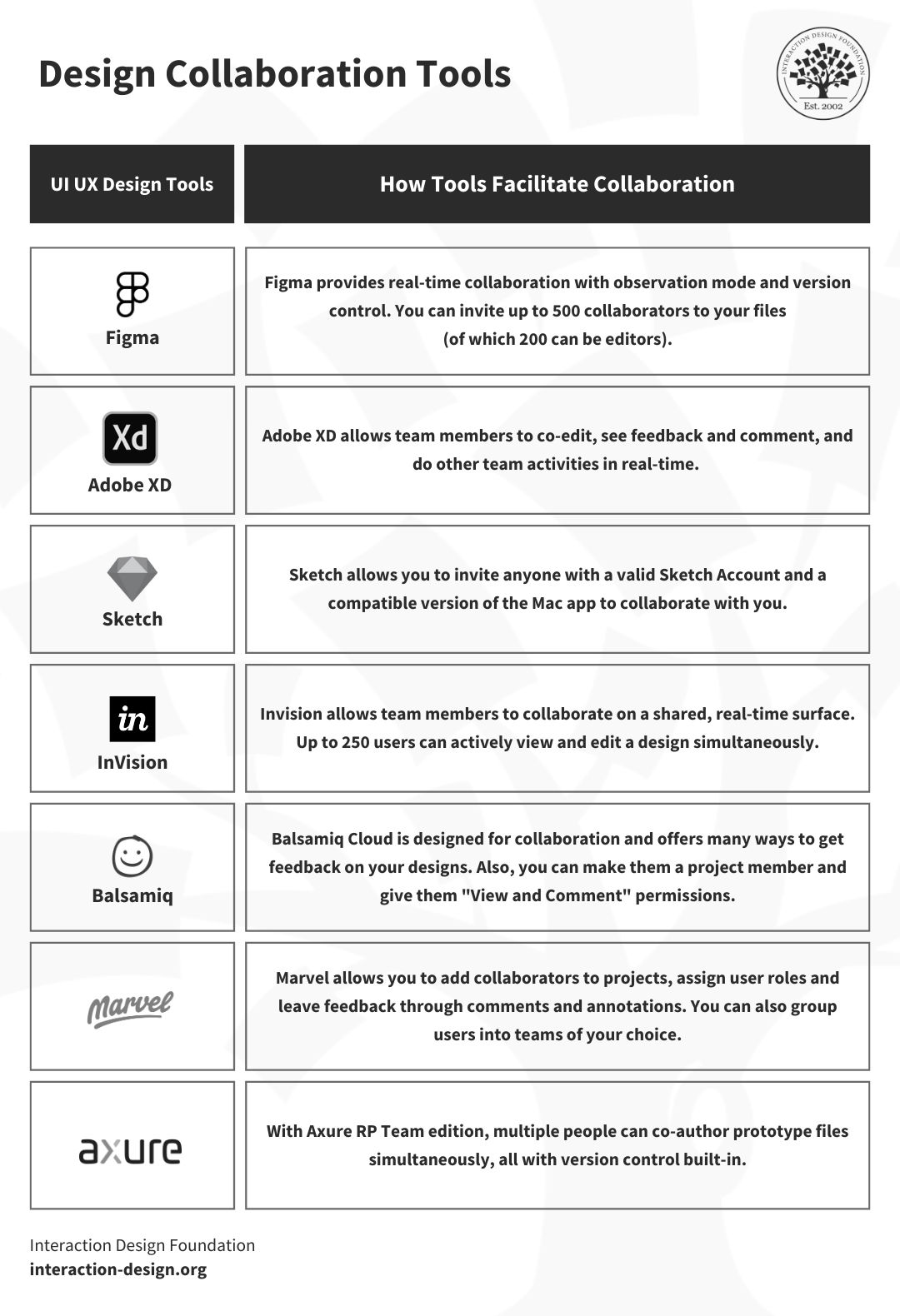
Figma—and this one’s a popular cloud-based design tool that’s known for its collaborative features—lets multiple designers work on a project at the same time, part of what makes it a go-to pick for design teams.
A neat—and ultra-helpful—point about Figma is how it supports advanced drawing tools, components, and real-time seamless collaboration—things you’ll be glad of when you’re using it and when you look back. Other juicy plusses are how you can create interactive wireframes within the application, its cloud-based nature is something that makes it accessible from any system that’s got a browser, and—what’s more—Figma promotes design asset management and provides design systems that put consistency forward across designs: pretty nifty.
So, what’s the cost to have this great tool at—and on—your side? Well, Figma offers a free tier for individuals, but if you’re after additional features, then Figma Professional is something you can get for $12 per editor/month and Figma Organization comes at $45 per editor/month.
2. Sketch
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 3.0 Source
Sketch is a vector graphics editor tool for macOS—and another popular pick—and one thing it’s known for is how it stands for simplicity and efficiency. It’s no surprise, then, that it sees such wide use in creating interfaces, icons, and web development.
Sketch has got some neat features that make it a hot choice on the go-to list—especially since it provides you with symbols and styles for reusable components, plugins for extended functionality. And an extensive plugin ecosystem offers you a highly customizable design experience and shared libraries for that (yes, ultra-important) team collaboration factor that you’ll tend to need on projects.
“How much?” you might ask; well, Sketch costs $99 a year—with a free trial available—the license includes updates for one year, and you can keep on using the last version you downloaded even after your license expires.
3. Axure RP
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 3.0 Source
Axure RP is a nice and solid, comprehensive tool if you’re in the market for wireframing, prototyping, and documenting design projects—and you probably will be. And its detailed specifications, documentation capabilities, and dynamic, conditional interactions are both neat qualities and points of recognition which people know Axure for.
There’s a great deal to like when you’ve got Axure RP, since it allows designers to create highly interactive and dynamic prototypes with conditional logic, variables, and adaptive views. And, on top of that, it supports collaborative editing and automated specification documentation, too, and its advanced interaction features make it ideal if you just happen to be involved in complex projects and are doing things like detailed prototyping.
The pricing model for Axure RP is that it offers a 30-day free trial and after that, the pricing starts at $25 per user/month for the pro edition and $42 per user/month for the team edition.
4. Balsamiq
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 3.0 Source
Next up—and not that this is in any particular order, mind you—we’ve got a popular wireframing tool that helps designers and product managers create mockups nice and fast. Plus—kind of mirroring that—it's designed to mimic the speed and simplicity you’d find when sketching on a whiteboard.
Balsamiq’s got a lot to offer features-wise, too, not least since it provides an extensive library of UI components and icons, drag-and-drop functionality, and sketch-style wireframes for a low-fidelity look. It’s a marvellous pick for those lower-fidelity prototypes. In any case, the simplicity factor—which is a big one when you’re involved in early-stage concept development, say—makes Balsamiq a good, solid place to start for beginners and a welcome go-to whenever you need to get a lo-fi wireframe or prototype done.
For Balsamiq, you get to enjoy a 30-day free trial, and then there’s pricing that starts at $9 monthly for two projects, with more extensive plans available for you to check out.
How About an In-Depth Review of a Top UX and UI Design Tool?
Sketch
Why did we choose Sketch?
We’ll pop the hood on one of our picks now and get into it in far more detail; and we’ll take Sketch as an example. One reason for why we like this one is how—if you compare it to some of its competitors—Sketch is lightweight, with a disk space of only 45MB. And it’s a point that makes it both a fast and responsive tool to use and a nifty asset to have your hands on when you’re in the design chair.
It’s a native Mac application, and it offers you an intuitive user interface that’s got a familiar (and customizable) toolbar, navigator, and inspector. And it’s something that makes it a nifty and accessible tool for beginners and experienced designers alike.
How does Sketch work?
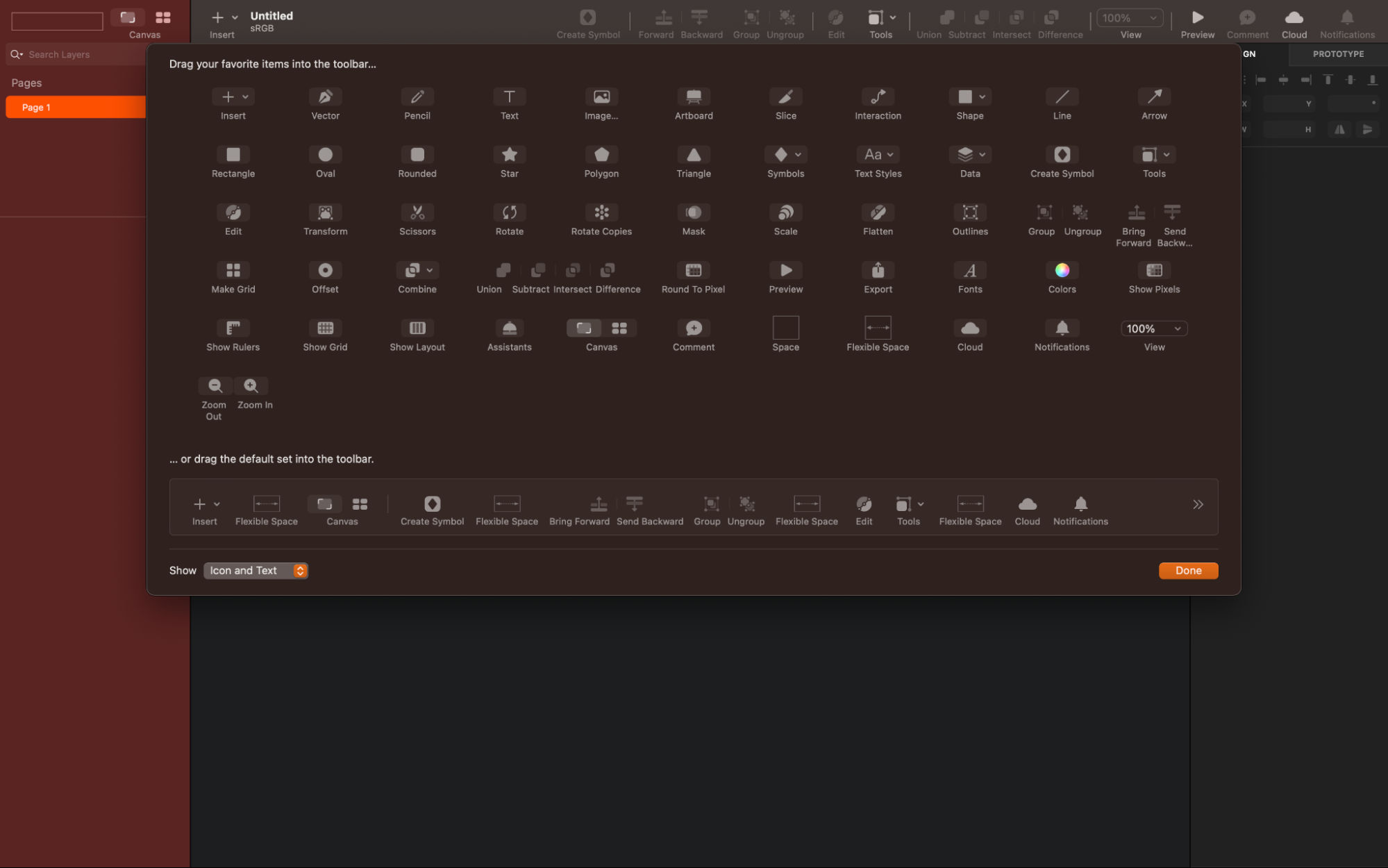
How to Customize Your Toolbar
What you do to start off is you personalize your toolbar so it suits your workflow. For that, right-click on the toolbar and select the tools you use frequently, and tools like symbols, scissors, outlines, and Round to Pixel might come in handy. Just check out the screenshot below to see what a customized toolbar looks like as an example.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 3.0 Source
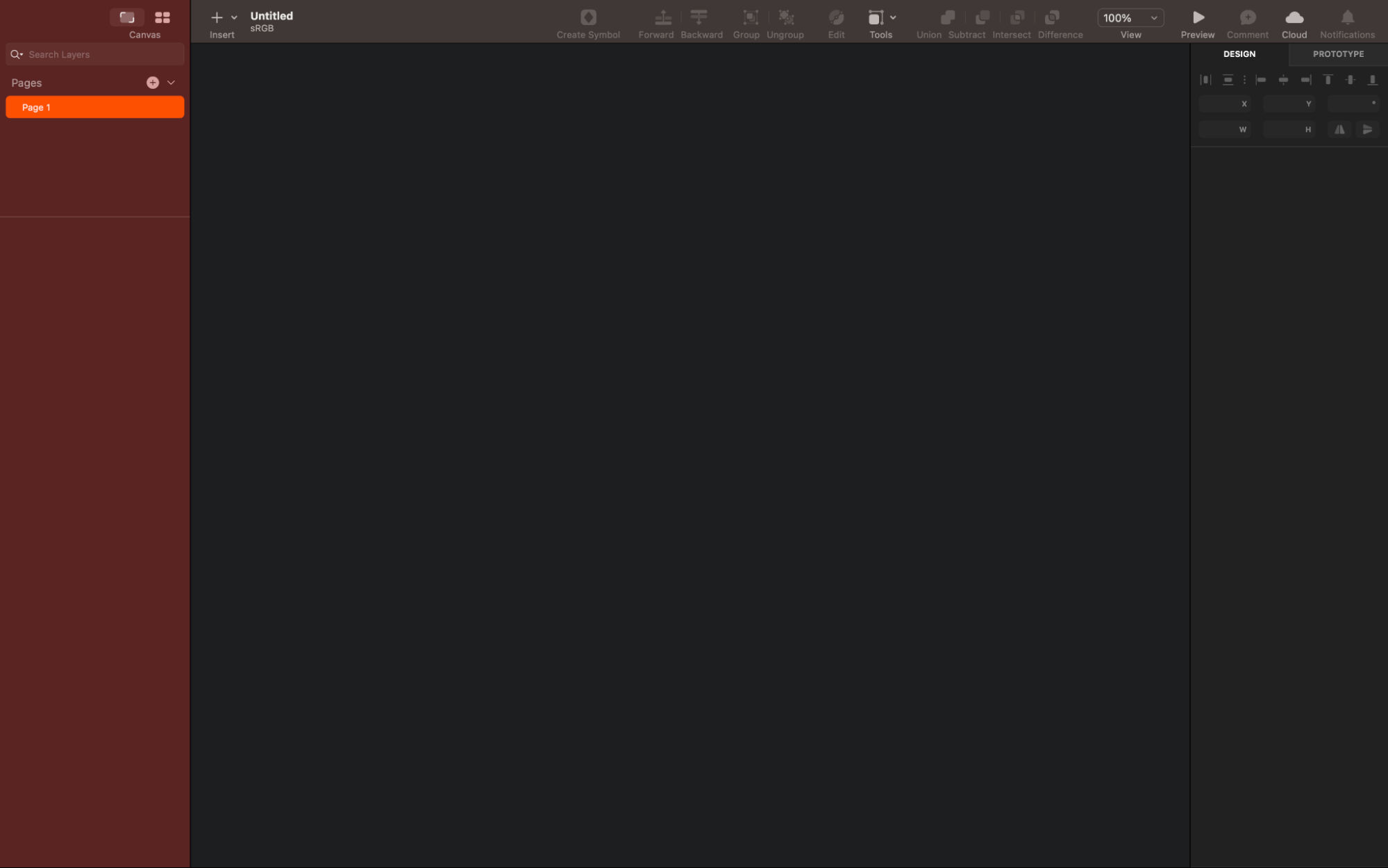
How to Use Artboards
One neat point about artboards is how they work as the screens of your application. To create a new artboard, first just press 'A'—and a list of preset screen sizes for various platforms will be up there in the top-right corner for your pleasure and decision-making. You can select any preset or create a customized size, and all your application screens can exist within a single Sketch file—and it’s a pretty neat plus that makes it easier to manage your project.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 3.0 Source
Pages
Pages in Sketch represent different platforms or resolutions. For example, you might’ve got one page for iOS designs and another for Android, and—that way—you can house an entire project within a single Sketch file. What’s more, you can switch between pages fast through the dropdown or the keyboard shortcuts Fn ↑ and ↓.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 3.0 Source
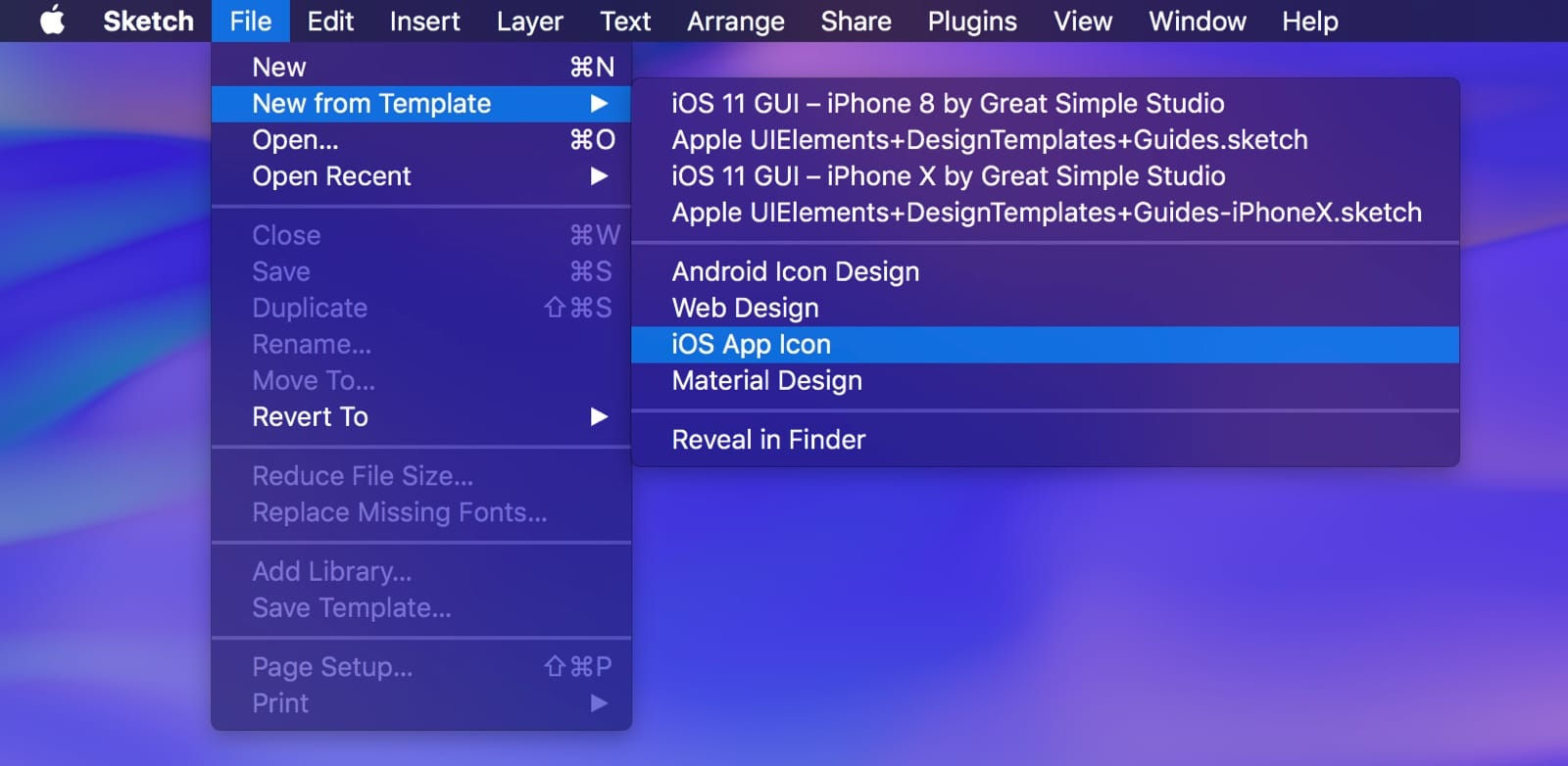
UI Templates
Templates are often a designer’s best friend—since it’s so nice when you’ve got something “prefabbed” to reach for. Sketch has got preloaded UI templates for iOS, Material Design, and Responsive Web which you can get to through File > New From Template—and you can add your own templates, downloaded from the web, too.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 3.0 Source
How to Design at 1x
When you’re designing for iOS, it's best to start at 1x resolution—and that’s preferably from using the iPhone 8 screen size as a reference (375 x 667 pt). Remember a little golden rule here that 1 px in Sketch equals 1 pt on the device screen.
Alignment, Distances, and Guides
Sketch provides you with various tools that help you design with precision, and Smart Guides help align your elements. The Distances feature measures the space between layers, and rulers help to create guides for your design.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 3.0 Source
Layout Settings
Layout settings allow you to set up your own grid system. It’s a nifty plus that’s especially useful whenever you’re designing for larger screens that call for clean divisions, and for those we can think of web interfaces or tablet screens.
How to Work With Text
To add text to your design, you press 'T' and the inspector lets you select the font and adjust the styles. Text styles in Sketch work similarly to CSS, which allows you to apply consistent styles across multiple text layers.
Preferences
Set up your preferences according to your needs—and this includes enabling Auto-Save to protect your work, adjusting Pixel Fitting for sharper designs, and setting up the color and gradient palettes which you find preferable.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 3.0 Source
Colors and Gradients
Use the color picker to pick and save your preferred colors. Sketch has got an eyedropper tool to pick colors with from anywhere within or outside the application as well. On a similar note, you can apply gradients to your designs to add depth and visual interest.
Remember, practice is key to mastering Sketch. So, do be sure to explore each feature thoroughly and experiment with different tools and settings to find out what works best for what you need to do as you move through your design process and produce deliverables that will not just function but resonate well, too.
The Take Away
Pick any trade where professionals create, modify, or fix something and it’s a foregone conclusion that tools are vital to the job. So is knowing how to use which ones for which tasks and, of course, all the principles and other theoretical essentials that the industry calls for a professional to know. The digital design business is no exception to that. Indeed, it can pay big dividends when you’ve got the right tools for the jobs you need to do as a UX or UI designer so you can work your way towards the most innovative and user-friendly designs to wow your target users and bring them closer to your brand.
Because the nature of the industry is tech-based, it takes keeping a finger on the pulse of the latest tools and technologies and an eye on which features can serve you best in a project. We've given you a list of some neat and handy—and popular—tools here.
We would love to hear from you about your experiences with these tools. You can share your thoughts, insights, and tips in the comments section. This will not only help us but also benefit the wider design community.
Remember, this article is an evergreen resource, and we'll be updating it regularly to reflect the newest trends and tools in the UX/UI design world. So, do check back often for the latest information.
As the UX/UI design field grows, so does the demand for skilled professionals. Whether you're starting out or looking to upskill, our courses can provide the knowledge and skills you need to excel in this exciting industry.
If you're new to the field, consider joining our beginner UX courses today!
Already have some experience? Enroll in our intermediate UX/UI courses to further hone your skills.
Stay creative, stay curious, and most importantly, keep designing!