UX Roles: The Ultimate Guide – Who Does What and Which One You Should Go For?
- 1.1k shares
- 1 mth ago
UX writing is the practice of creating the text in a user experience. It aims to improve user experience by informing and engaging the user. Examples of UX writing include notifications, titles, buttons, instructions, labels, descriptions, controls and warnings.
In this video, UX writer and author Torrey Podmajersky explains what UX content is (UX writing being a main component of it), the different forms it takes and where it fits in the cycle that engages the user.
UX writing is essential for seamless and intuitive user experiences and helps eliminate pain points. When done well, it can help users navigate a product more easily, understand its features, and accomplish their goals more efficiently. On the other hand, poorly written copy can lead to confusion, frustration, and ultimately, a negative user experience.
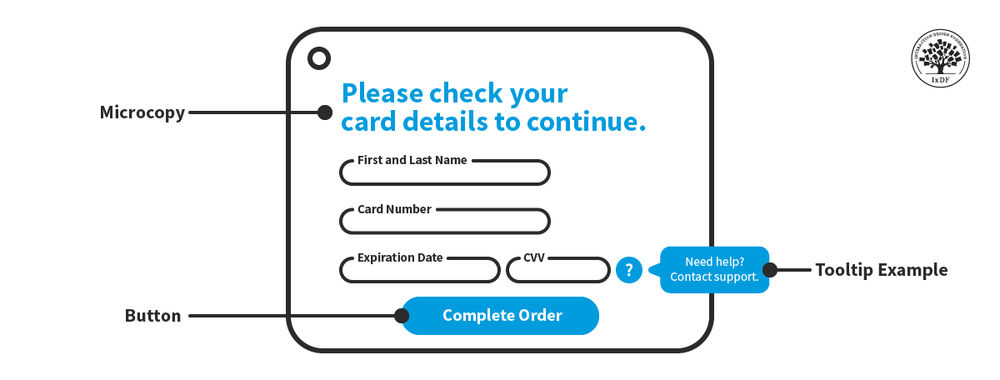
Microcopy is small pieces of text within a user interface that help users understand how to use a product or service, like button labels, form field instructions, error messages, and other short snippets of text that guide the user through the user experience. Accordingly, microcopy falls under the umbrella of UX writing.
Examples of microcopy on Airbnb’s mobile app.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0 and Airbnb, Fair Use
Language and text have always been part of digital products and user experiences, but previously they needed manuals, generally written by technical writers. The product's usability depended on the manual's quality, in other words, how clear and concise the manual was. These manuals eventually developed into online help and other forms of “user assistance”.
With the rise of user-centered design, intuitive experiences and increasingly complex digital products, so came the need for UX writing. Now we can navigate user experiences without a manual.
In the 2000s and especially the 2010s, UX writing became its own discipline and position within design.
Here are some key factors that have contributed to the growth of UX writing as a distinct field:
The growth of mobile and web-based applications: The proliferation of mobile apps and web-based applications has resulted in the exponential growth of UX writing.
The rise of user-centered design: As digital products and services have become more user-centric, the need for clear and compelling language in interfaces has become increasingly important. UX writing has emerged as a way to ensure that the language in a digital product is clear and effective and consistent with the brand's voice and tone.
The increasing importance of brand voice: It is more crucial than ever to have a consistent brand voice across all channels, including digital products. That means that UX writing has become an important part of brand strategy. UX writers work closely with brand managers and marketers to ensure that the language in a digital product is consistent with the brand's overall messaging.
The recognition of the value of good UX writing: As companies have recognized the impact that good UX writing can have on user engagement and satisfaction, the demand for UX writers has grown. Many companies now have dedicated UX writing teams or hire freelance writers to work on their digital products.
Effective UX writing is a crucial element of a positive user experience for digital products and services. Here are a few reasons why UX writing is so important:
Clarity and understanding: Good UX writing ensures that users understand what they see on their screen and how to interact with it. Clear and concise language helps users to navigate a digital product or service with ease, which reduces frustration and increases engagement.
Consistency: Consistent language and terminology throughout a digital product or service can reinforce the user's understanding of the product's functionality and build trust. If you use one word to describe a particular term, ensure that the same word is used throughout the experience. Additionally, a consistent brand voice also helps to strengthen the user's relationship with the brand.
Accessibility: UX writing can make a digital product more accessible to users with disabilities and by extension, better for all users. For example, there should be text for all elements (icons, buttons and other affordances) so that screen readers and other assistive technologies can pick them up.
Tone and personality: A well-crafted tone and personality in the language of a digital product can create an emotional connection with users, which builds brand loyalty and increases user engagement.
Localization: Good UX writing recognizes the nuances of language and culture in different regions of the world—digital products should have different versions depending on the user’s location and language.
Dribbble’s 404 page is colorful and playful. The numbers, 404, are made up of a collage of different designs of the same color. It has a slider just below it which lets you change the designs and the color of the numbers! The copy, interactive element and usability of the page are all consistent with Dribbble’s brand. It’s playful and has personality, while still highlighting the creators.
© Dribbble, Fair Use
UX writing is an integral part of a product and as such, UX writers or content designers should be involved in every step of the UX design process.
The approach will vary depending on the team, organization, budget and other factors, but ideally, UX writers will collaborate with designers, researchers, and other stakeholders early in the design process to understand user needs and business goals. This collaboration helps to ensure that the language in the product is consistent with the overall design and aligns with the user's expectations.
As the design process progresses, UX writers work closely with designers to ensure that the language used in the interface is clear, concise and useful. The team will test their language choices to ensure that users can easily understand and interact with the product.
UX writing is more than simply writing text; it should also create a harmonious brand voice and tone throughout the product. This involves collaborating with brand managers and marketers to ensure that the language in the product aligns with the brand's overall messaging and tone.
UX writers will also work with developers and product managers to ensure that the language and UX content is implemented correctly in the final product. This collaboration helps to ensure that the language in the product is not only clear and effective but also practical.
User experiences need to be intuitive and easy to use if they’re going to succeed. UX writing plays a significant role in a digital product's usability, so good UX writing is essential for an overall positive user experience. With consistent, clear and accessible language, UX writers can help to increase user engagement, build trust and strengthen brand loyalty.
Watch UX writer and author Torrey Podmajersky’s Master Class UX Writing: How To Use Words As A Design Power Tool.
Check out Nielsen Norman Group’s UX Writing Study Guide.
Read Torrey Podmajersky’s book on UX Writing, Strategic Writing for UX: Drive Engagement, Conversion, and Retention with Every Word.
Discover Nick Babich’s 16 Rules of Effective UX Writing.
UX writing focuses on creating copy that enhances the user experience within digital products. It guides users with clear, concise instructions, and information. It differs from traditional copywriting, which usually aims to advertise or market products and services. UX writers craft text for user interfaces, to help users navigate apps or websites effortlessly, whereas traditional copywriters focus on persuading or engaging the audience with the brand. UX writing requires an understanding of user psychology and design principles to create intuitive and helpful copy that fits seamlessly within the user's journey, emphasizing usability and accessibility.
Learn more about UX writing in the Master Class UX Writing: How To Use Words As A Design Power Tool.
The key principles of effective UX writing include clarity, conciseness, and context. UX writers must ensure that their copy is clear and avoids jargon and technical terms that could confuse users. Conciseness is crucial; every word should serve a purpose, helping users understand their next steps without overwhelming them with unnecessary information.
Context matters significantly in UX writing; the copy should be relevant to the user's current task or stage in the user journey, providing guidance and feedback that is timely and useful. Additionally, UX writing should always aim to be user-centered, focusing on the needs and understanding of the user, enhancing the overall usability and accessibility of the digital product.
Learn more about UX writing in this article How to Get Started with UX Writing.
UX writing improves user experience by guiding users through digital products with clear, concise, and useful text. It reduces user confusion by providing straightforward instructions and feedback, enhancing the usability and accessibility of websites and apps. Effective UX writing helps users complete tasks efficiently, increasing overall satisfaction and engagement with the product. By focusing on the user's needs and context, UX writing plays a pivotal role in creating intuitive interfaces that foster positive interactions and build trust between the user and the digital product.
Learn more about UX writing in this article How to Get Started with UX Writing.
Best practices for creating clear and concise UX copy include using simple and direct language that avoids jargon and technical terms. Aim for brevity by eliminating unnecessary words and focusing on essential information. Structure content logically, using headings and bullet points to break up text and make it easy to scan. Tailor the tone and vocabulary to the target audience, ensuring it resonates and is accessible. Employ active voice to make instructions dynamic and direct. Finally, test copy with real users to ensure clarity and effectiveness, refining based on feedback to meet user needs precisely. These practices ensure UX copy enhances the user experience by being easily understandable and actionable.
Learn more about UX writing in the Master Class UX Writing: How To Use Words As A Design Power Tool.
You measure the success of UX writing by evaluating user engagement, conversion rates, and usability test outcomes. Track user interactions to see if the copy leads to the desired actions, such as clicking a button or completing a form. Analyze conversion rates to determine if the UX writing effectively guides users through the conversion funnel. Conduct usability tests to gather direct feedback on how well the copy helps users navigate and understand the product. Also, monitor customer support inquiries to identify if users are facing issues that could be resolved with clearer UX writing. Success in UX writing is evident when users can effortlessly achieve their goals, leading to increased satisfaction and reduced confusion or frustration.
Learn more about UX writing in the Master Class UX Writing: How To Use Words As A Design Power Tool.
Watch the trailer here:
Podmajersky, T. (2019). Strategic Writing for UX. O'Reilly Media, Inc.
Metts, M. J., Welfle, A., & Madden, N. (Illustrator). (2020). Writing Is Designing: Words and the User Experience. Rosenfeld Media.
Fenton, N., & Lee, K. (2014). Nicely Said: Writing for the Web with Style and Purpose (1st ed.). New Riders.
UX writing plays a pivotal role in the design process by shaping user interactions and guiding users through digital products. It ensures that all textual content—from buttons and menus to error messages and help guides—communicates clearly, enhancing usability and user satisfaction. UX writers collaborate with designers, developers, and stakeholders from the early stages, contributing to wireframes, prototypes, and user testing. Their insights help refine the user journey, making complex systems understandable and navigable. By focusing on the user's perspective, UX writing drives the creation of intuitive, accessible interfaces that support the overall goals of the product.
Learn more in Torrey Podmajersky’s book, Strategic Writing for UX.
UX writers can collaborate effectively with designers and developers by participating in all stages of the design process, from initial concept to final testing. They should communicate regularly, sharing insights and feedback through meetings and design reviews. Utilizing collaborative tools like shared documents and design platforms facilitates real-time feedback and iteration. UX writers also need to understand design and development constraints, working closely with the team to craft text that fits within the user interface and aligns with technical capabilities. Establishing clear guidelines for tone, style, and terminology ensures consistency across the product. By actively engaging in the project lifecycle and fostering open communication, UX writers, designers, and developers can create cohesive, user-centered experiences.
Learn more about UX writing in the Master Class UX Writing: How To Use Words As A Design Power Tool.
Essential tools and resources for UX writers include content management systems (CMS) for publishing and updating content, design and prototyping tools like Sketch, Figma, and Adobe XD for collaborating with designers, and version control systems such as GitHub to manage and track changes in content. Text editing and grammar tools like Grammarly and Hemingway ensure clarity and readability. UX writers also benefit from user research tools to gather insights on language and terminology that resonate with users. Additionally, style guides and design systems help maintain consistency across the product. Access to analytics tools to evaluate the effectiveness of the copy in driving user actions is crucial for refining and improving UX writing.
Learn more in Torrey Podmajersky’s book, Strategic Writing for UX.
You create a consistent voice and tone in UX writing by first defining your brand's personality and how it should communicate with users. Develop a style guide that outlines this voice and tone, providing specific examples and guidelines for different types of content. Ensure all UX writers and content creators have access to and understand this style guide. Regularly review and update your content to maintain consistency as your product and brand evolve. Train your team on the importance of voice and tone in user experience, and encourage them to use the style guide as a reference in their work. Consistently applying these guidelines across all user interactions helps build a recognizable and trustworthy brand identity.
Learn more about UX writing in the Master Class UX Writing: How To Use Words As A Design Power Tool.
Remember, the more you learn about design, the more you make yourself valuable.
Improve your UX / UI Design skills and grow your career! Join IxDF now!
You earned your gift with a perfect score! Let us send it to you.
We've emailed your gift to name@email.com.
Improve your UX / UI Design skills and grow your career! Join IxDF now!
Here's the entire UX literature on UX Writing by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Take a deep dive into UX Writing with our course UX Management: Strategy and Tactics .
Master complex skills effortlessly with proven best practices and toolkits directly from the world's top design experts. Meet your experts for this course:
Frank Spillers: Service Designer and Founder and CEO of Experience Dynamics.
Alison Gavine: Managing Partner and Global User Research Director at Experience Dynamics.
Daniel Loewus-Deitch: UX Leader, Media Psychologist, and Assistant Vice President, User Experience at Unum.


We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge. Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change, , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge!
